Powering AI Agents with Context:
DataHub Town Hall Highlights
AI agents have moved from proof-of-concept to production roadmaps. As practitioners plan their agentic workflows, we’ve been listening to what they want to build and the problems they encounter as they do:
“The SQL our agent generates is close, but it doesn’t understand what ‘LTV’ means to our team so it pulls from the wrong tables.”
“We have a runbook for root-causing this kind of data incident. Can we make that accessible to the agent so it self-solves next time?”
“I want to build an agent that periodically generates a report of every table and pipeline handling sensitive data.”
These are the kinds of workflows teams are ready to automate, but only if agents can access the full context behind their data. When metadata, documentation, lineage, and governance rules live in separate systems, agents work with incomplete information. They generate inaccurate SQL, miss critical assets, and can’t reason about your data the way your team does.The January 2026 DataHub Town Hall addressed this production readiness gap. New releases unify unstructured and structured data, bring DataHub context into your agent workflows, enable end-to-end orchestration from a single interface, and accelerate time-to-value.
Expanding the context graph: Semantic search and unstructured data
Understanding data requires more than schemas and lineage. Teams need business logic, documentation, term definitions, and institutional knowledge from runbooks. This context exists in Notion, Confluence, and internal wikis, but it’s disconnected from the data catalog where teams actually search for information about data.
DataHub’s context graph bridges this gap by bringing together data and knowledge, unifying documents, datasets, pipelines, dashboards, and more. With DataHub, users can discover and search context from unstructured data sources alongside structured data assets, rather than hunting across multiple tools to piece together understanding.
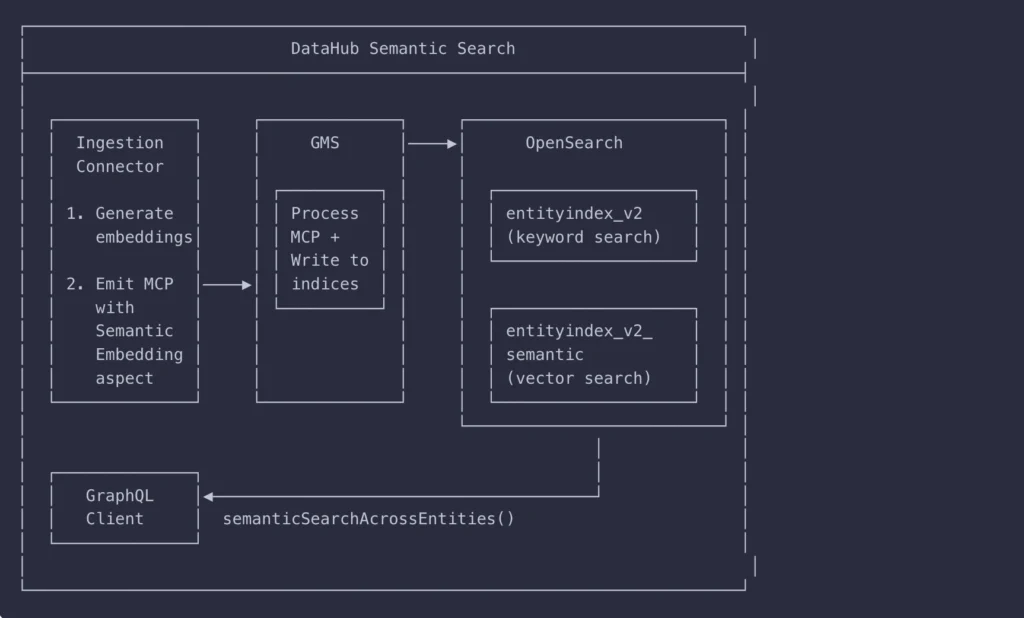
Semantic search enabled
DataHub now chunks and embeds text documents during ingestion, enabling semantic search alongside traditional keyword search. Semantic search enables agents to find relevant context based on meaning rather than relying on exact keyword matches.
The platform supports AWS Bedrock, OpenAI, and Cohere as embedding providers. Ingestion connectors help you produce semantic embeddings for documents, making it easy to bring in unstructured context on your own or take advantage of DataHub’s out-of-the-box connectors.
Agents access embeddings through DataHub’s API surface area:
- GraphQL for programmatic access
- MCP tools for agent integrations
- Ask DataHub for conversational queries in DataHub Cloud
For a deeper dive, read our documentation about configuring semantic search for DataHub OSS (available v1.4.0+).
Notion and Confluence context integrated
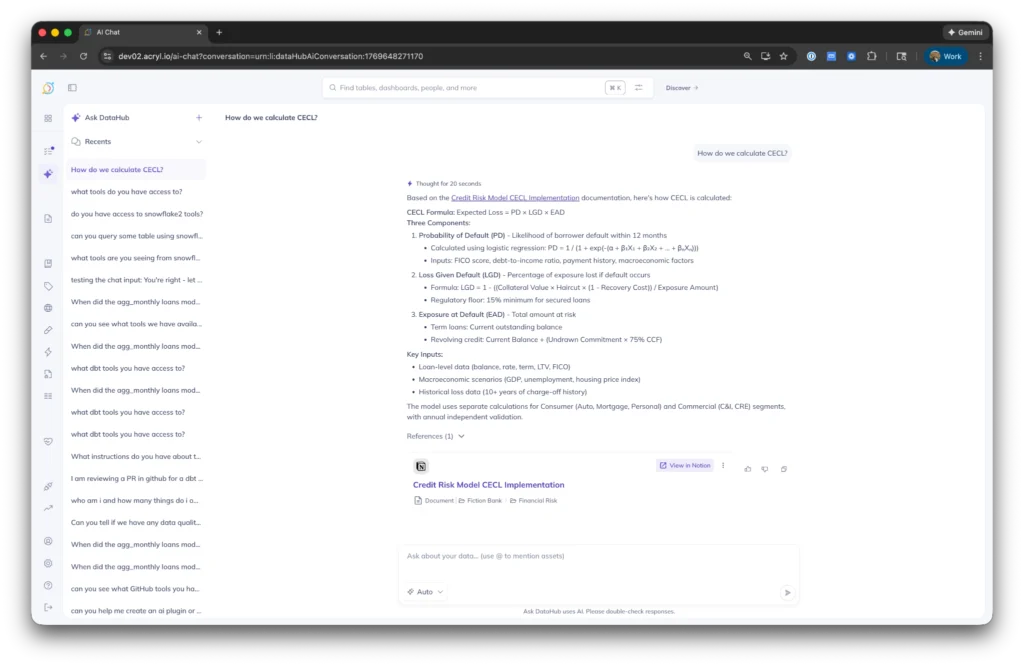
The Notion and Confluence connectors bring workspace content into DataHub’s semantic search index. With your data and your data knowledge base together in one place, inclusive of runbooks, FAQs, decision history, business definitions, and more, DataHub enables you to answer a broader set of questions without leaving the platform.
When agents need to understand “how do we calculate monthly loan aggregations” or “what’s our GDPR deletion policy,” Ask DataHub answers questions that span technical schemas and business logic stored in Notion and Confluence. No more context switching between your data catalog and documentation tools.
Availability: Releasing in DataHub Core 1.4.0
Power your AI agents with DataHub context
Agent Context Kit
If you’re building and deploying agents in other platforms like Snowflake Intelligence, LangChain, or Crew.ai, DataHub’s Agent Context Kit helps you bring context and capabilities to your agent.
The kit packages DataHub’s capabilities as tools that work in any agent framework, enabling agents to:
- Find the right tables and columns to query in conversational data analytics agents
- Make data changes with confidence via DataHub’s rich lineage graph
- Debug data incidents and assertion failures across tools like GitHub, dbt, Snowflake, and more
These capabilities integrate with:
- MCP Server: Connect Claude and other AI assistants to DataHub via Model Context Protocol
- Snowflake Cortex: Execute Text-to-SQL queries with DataHub context directly in Snowflake
- LangChain: Use DataHub tools in custom LangChain agents
- Coming soon: Google ADK, OpenAI, CrewAI
Supercharging Snowflake Intelligence agents with DataHub context
Snowflake Intelligence provides powerful text-to-SQL capabilities, but by default it sees little beyond structural information: table names, column names and types, and basic statistics. DataHub adds the context that makes those capabilities trustworthy.
With the Agent Context Kit CLI for Snowflake, you can create Snowflake Intelligence agents that have built-in tools for accessing the rich semantic information stored in DataHub, such as data descriptions, domains, glossary terms, lineage, data quality, and more. The connector searches documents and assets, reads Snowflake data tables, and generates queries to answer user questions.
The result: an agent that doesn’t just query Snowflake, it reasons about your data the way your team does, by understanding the broader business context BEFORE generating SQL. You get accurate answers you can trust and confident actions that won’t break downstream dependencies.
Example: Imagine we work at a bank. A user asks the agent: “Generate a query to calculate the amount of commercial real estate loans that meet our ‘safe’ loan-to-value criteria.”
This requires understanding:
- What loan-to-value ratio means
- What loan types are offered by the bank
- What “safe” means
All unstructured knowledge that is probably captured in your docs somewhere.
The agent uses this semantic understanding when generating SQL to ensure that the SQL follows the guidelines set by the bank.
To complete this workflow, the agent:
1. Searches across documents to understand the business definitions required to generate SQL
2. Finds trustworthy tables and columns that can answer the question based on popularity (referencing query history), table freshness, and table lineage
3. Generates SQL that embeds the semantic understanding from Step 1
4. Executes
Availability: Releasing in DataHub Core 1.4.0
Building LangChain agents with DataHub context
Agents can hallucinate, guess at metrics, and make up business logic. DataHub improves the situation by giving LangChain agents direct access to your context, including actual tables, columns, documents, metric definitions, lineage relationships, governance rules, and documentation.
The result: agents reason with a semantic understanding about your data. You get accurate answers grounded by the tribal knowledge around your business.
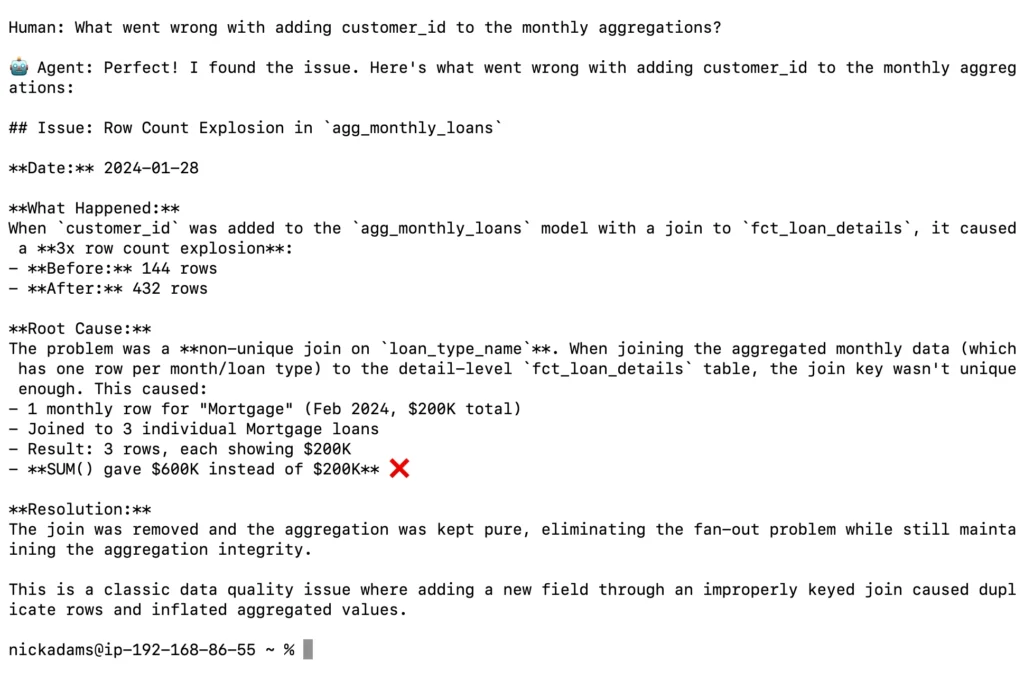
Example: A user asks “what went wrong with adding customer_id to monthly aggregations?” The agent:
- Looks up documentation in Notion and Confluence
- Identifies an incident log about the agg_monthly_loans table from a row count explosion in January 2024
- Queries the tables to determine the explosion caused incorrect sums
- Explains: “Before: 10 rows. After: 30 rows (3x difference).”
Availability: Releasing in DataHub Core 1.4.0
The next frontier: Unlocking data workflows across siloed tools
Data practitioners don’t work in a single tool. Workflows span multiple systems, and context gets lost when you switch between them:
- Debugging data quality issues: Check assertion failures in DataHub, review recent code changes in GitHub, inspect dbt build logs, and run diagnostic queries in Snowflake
- Text-to-SQL with proper context: Find relevant tables using DataHub metadata, construct queries informed by documentation, and execute in Snowflake or Databricks
- GDPR compliance: Understand deletion policies from internal docs, identify tables with user data using DataHub, and execute deletion queries in Snowflake
Ask DataHub plugins solve this by bringing GitHub, Snowflake, dbt, and other tools into the conversation. Instead of forcing you to context-switch between your data catalog and the systems where work happens, Ask DataHub orchestrates workflows across all of them.
Example: A data quality assertion fails on the agg_monthly_loans table. You ask Ask DataHub what happened. The workflow:
1. Searches GitHub and dbt Cloud for recent changes
2. Identifies a PR merged on January 27 that introduced a join logic bug
3. Confirms that despite the bug, the dbt model built successfully
4. Raises a PR to revert the bad change in your name
The entire debugging workflow from assertion failure to fix happens in one conversation without switching tools.
Availability: Private beta in DataHub Cloud v0.3.17. Reach out to your DataHub rep to participate.
Configure connections to data sources with assistance
For DataHub Cloud customers, Ask DataHub now integrates directly into ingestion configuration screens, helping you connect to data sources faster.
You can use Ask DataHub throughout ingestion to:
- Get help finding credentials and connection details without leaving the page
- Generate regex patterns for filtering tables based on naming conventions
- Understand configuration options and their performance trade-offs
- Diagnose ingestion failures with plain-language explanations
“We want to make it as easy as possible for people to get up and running with ingestion and get things moving. We’re making it very easy for users to identify ingestion issues, interpret what’s happening, and act on it.”
— Maggie Hays, Founding Product Manager, DataHub
When an ingestion run fails, Ask DataHub scans the full error logs and explains what happened in plain language. For a failed Snowflake connection, it might tell you: “Authentication failed. The username provided doesn’t exist in this Snowflake account. Check that you’re using the correct account identifier and username format.”
Availability: DataHub Cloud v0.3.16 (live now)
RFC: Bringing AI agents and related assets into the DataHub metadata model
As AI moves into production, new classes of AI-native assets are emerging: vector databases, agents, prompts, and more. These assets are multiplying fast, but most organizations have no systematic way to discover, govern, or understand how they connect to existing data.
DataHub opened an RFC to address this: a proposal to model these concepts directly inside DataHub so you can catalog, search, and contextualize AI assets alongside all of your data.
“People are worried about not understanding what kind of sprawl is being created and worrying about discoverability of those assets themselves. Maybe there are a lot of very interesting agents that have been built in the company, but people don’t know about them, and so they can’t actually take advantage of them. And then there are the usual concerns that we’ve seen with data that we’re seeing playing out with AI agents: the importance of understanding trust, understanding quality, and understanding lineage.”
— Shirshanka Das, Co-Founder and CTO, DataHub
Join the discussion on GitHub or provide feedback in the #ai channel in the DataHub Slack community.
Introducing DataHub Cloud free trials
DataHub Cloud now offers a 21-day free trial with full access to the Ask DataHub AI assistant. The trial loads sample data immediately, so you can explore end-to-end lineage, test Ask DataHub, and understand the platform before connecting your own sources.
The trial includes:
- Pre-configured sample data showing lineage, datasets, and metadata features
- Full Ask DataHub access embedded throughout the interface
- Ability to ingest your own metadata during the trial period
- Guided onboarding with task-based navigation
Start your free trial to get hands-on experience with discovery, lineage, governance, observability, and DataHub Cloud’s new AI features. No commitment required.
Join the community building the future of context management
We’re building DataHub as your partner for the long term, not just the next release. The community drives our roadmap through RFCs, feedback in the DataHub Community Slack channel, and the production challenges you bring to town halls. What you’re building teaches us what to build next.
Three ways to get started:
- Watch the full town hall recording to see live demos of the free trial, Snowflake and LangChain integrations, and Ask DataHub plugins
- Join the DataHub Slack community to connect with practitioners building agentic workflows and test new features before they’re released
- Start your 21-day free trial to experience Ask DataHub, explore sample data, and test use cases with your own metadata
Recommended Next Reads